
You can confirm your new overclock using a program such as CPU-Z. To enabled XMP, simply select one of the profiles, save your settings and reboot. It offers up to three XMP profiles as standard and a further two customisable user profiles.
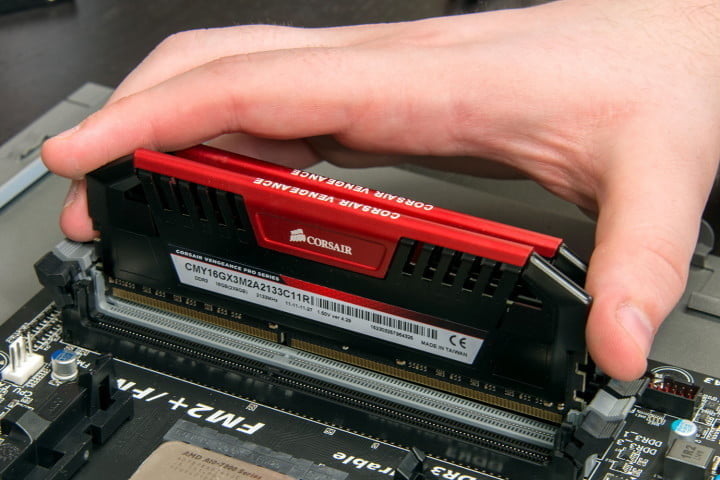

These profiles may provide different levels of overclocking, which can all be checked via the BIOS. XMP profiles can be accessed from within the BIOS on supported motherboards. XMP profiles essentially allow high-performance RAM, which run above industry DDR specifications, to be appropriately set up for your system.

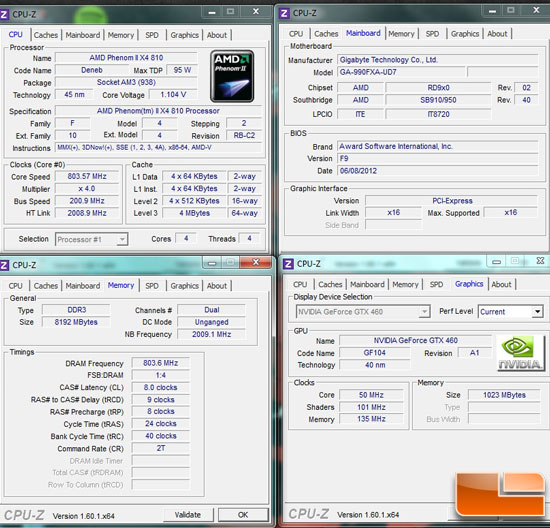
It also corrects for the extra voltage required which provides a stable overclock with the click of a button. XMP is an extension of SPD which provides higher frequencies and tighter timings for your memory to run at. Your BIOS will use a small chip on your RAM modules called an SPD (serial presence detect) chip to set memory timing and frequencies properly. Your computer needs to know the model of your RAM as well as which timings and frequency to set. Part of this process includes automatically configuring installed hardware, including your memory. It can be downloaded to your computer from various websites and provides detailed information about your computer, including the front-side bus speed.įor example, in the picture below, you can see that the bus speed is 99.79 MHz, which means this system has a 100 MHz bus speed.When you power on your computer, it conducts a power-on self-test. One free program that is worth checking out is CPU-Z. Some of these programs are free and some require payment. Many software programs are available over the Internet that list the speed of the front-side bus. You can find the memory bus speed, as well. Detailed specs of the motherboard should include the front-side bus speed, measured in MHz. Locate the model number of your computer's motherboard and search for the manufacturer and model number on the Internet. To determine the front-side bus speed on your computer, there are two primary options: Motherboard documentation But generally speaking, a faster bus means a faster computer. That works up to a point and can't make up for slow processors.

In general, the faster the bus speed, the faster the computer. The Northbridge "bridges" the gap between the CPU and RAM and the two communicate via the two buses. The front-side bus is what connects the computer processor (CPU) to the Northbridge, which then connects to the computer memory ( RAM) via the memory bus.
When discussing bus speed, the front-side bus is what is being referred to, but another important bus speed reference is the memory bus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
